Color theory is a powerful tool for enhancing the visual impact of your photographs. Understanding how colors interact, complement, and contrast can help you create more dynamic and aesthetically pleasing images. This guide explores key color theory principles and how to apply them to improve your photography.
Understand the Color Wheel
The color wheel is a fundamental tool in color theory that illustrates the relationships between colors:
- Primary Colors: Red, blue, and yellow are the building blocks of all other colors. They are placed equidistantly on the wheel.
- Secondary Colors: Green, orange, and purple are created by mixing primary colors. They sit between the primary colors on the wheel.
- Tertiary Colors: These are created by mixing a primary color with a secondary color, resulting in hues like red-orange or blue-green.
Familiarizing yourself with the color wheel helps you understand color relationships and how to use them effectively in your photography.
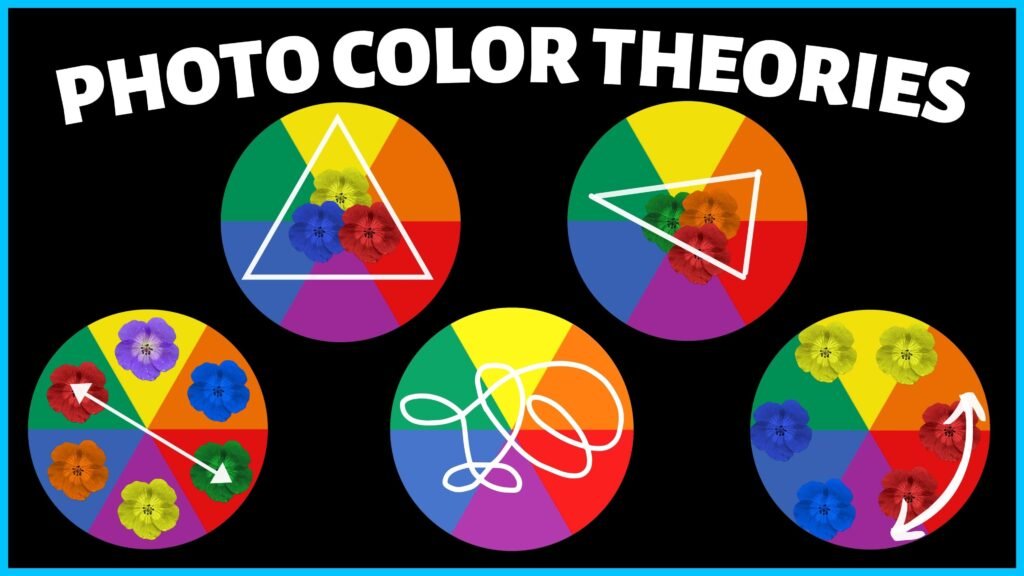
Use Complementary Colors
Complementary colors are pairs of colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel, such as blue and orange or red and green:
- Contrast and Vibrancy: Complementary colors create strong contrast and make each color appear more vibrant. Using these pairs can make your subject stand out and add visual interest.
- Color Balance: Incorporate complementary colors in balanced proportions to avoid overwhelming the viewer with too much contrast.
Incorporating complementary colors can enhance the impact of your images and draw attention to key elements.
Apply Analogous Colors
Analogous colors are adjacent to each other on the color wheel, such as blue, blue-green, and green:
- Harmony and Unity: These colors create a harmonious and cohesive look, making them ideal for achieving a soothing and visually appealing effect.
- Gradients and Transitions: Use analogous colors to create smooth transitions and gradients in your photos, enhancing the overall sense of unity.
Analogous colors are useful for creating a serene and well-coordinated color scheme in your photography.
Explore the Rule of Thirds with Color
The rule of thirds is a compositional technique that divides the image into a grid of nine equal parts:
- Color Placement: Apply the rule of thirds by positioning your subject or key color elements along the grid lines or at their intersections. This creates a balanced and engaging composition.
- Color Emphasis: Use the grid to emphasize specific colors or areas in your image, ensuring they capture the viewer’s attention.
Combining the rule of thirds with color placement enhances the visual impact and balance of your photos.
Leverage Color Temperature
Color temperature refers to the warmth or coolness of a color:
- Warm Colors: Reds, oranges, and yellows create a warm and energetic feel. They can be used to evoke emotions like warmth and excitement.
- Cool Colors: Blues, greens, and purples convey a calm and tranquil atmosphere. They are effective for creating a serene and relaxed mood.
Adjusting color temperature based on the mood you want to convey can significantly influence the emotional impact of your photos.
Use Monochromatic Color Schemes
A monochromatic color scheme involves using variations of a single color, such as different shades and tints of blue:
- Simplicity and Elegance: Monochromatic schemes create a clean and sophisticated look. They are effective for highlighting textures and patterns without the distraction of multiple colors.
- Focus and Depth: Use variations in lightness and darkness to add depth and contrast within a single color palette.
Monochromatic color schemes are useful for creating a cohesive and elegant visual effect in your photography.
Experiment with Color Filters and Editing
Color filters and editing tools can further enhance your color choices:
- Filters: Use filters to adjust the overall color balance and mood of your images. Experiment with different filters to find the effect that best suits your subject.
- Editing Software: Programs like Adobe Lightroom and Photoshop offer advanced color correction and enhancement tools. Adjust saturation, hue, and contrast to refine your color palette.
Editing tools allow for precise adjustments and creative exploration of color in your photos.
Conclusion
Applying color theory to your photography can significantly enhance the visual appeal and emotional impact of your images. By understanding the color wheel, using complementary and analogous colors, and experimenting with color temperature and filters, you can create more dynamic and engaging photographs. Embrace these techniques to improve your photographic skills and make your images stand out.






